What Are Low-Fidelity Wireframes?
Wireframes play a crucial role in the early stages of creating websites and applications. They serve as blueprints, providing a visual representation of the layout and structure before moving into the detailed design phase. One particular type of wireframe that holds immense value is the low-fidelity wireframe. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the definition of low-fidelity wireframes, explore their benefits, learn how to create them and discover best practices for their effective use. So, let’s dive in!
What Are Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Definition of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Low-fidelity wireframes, also known as lo-fi wireframes, are simple and rough sketches that outline the basic elements and structure of a webpage or application. They are intentionally kept minimalistic and lack intricate details, allowing designers to focus on the overall layout rather than aesthetics. These wireframes typically use basic shapes, lines, and placeholders to represent different components such as buttons, text blocks, images, and navigation menus.
The Importance of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
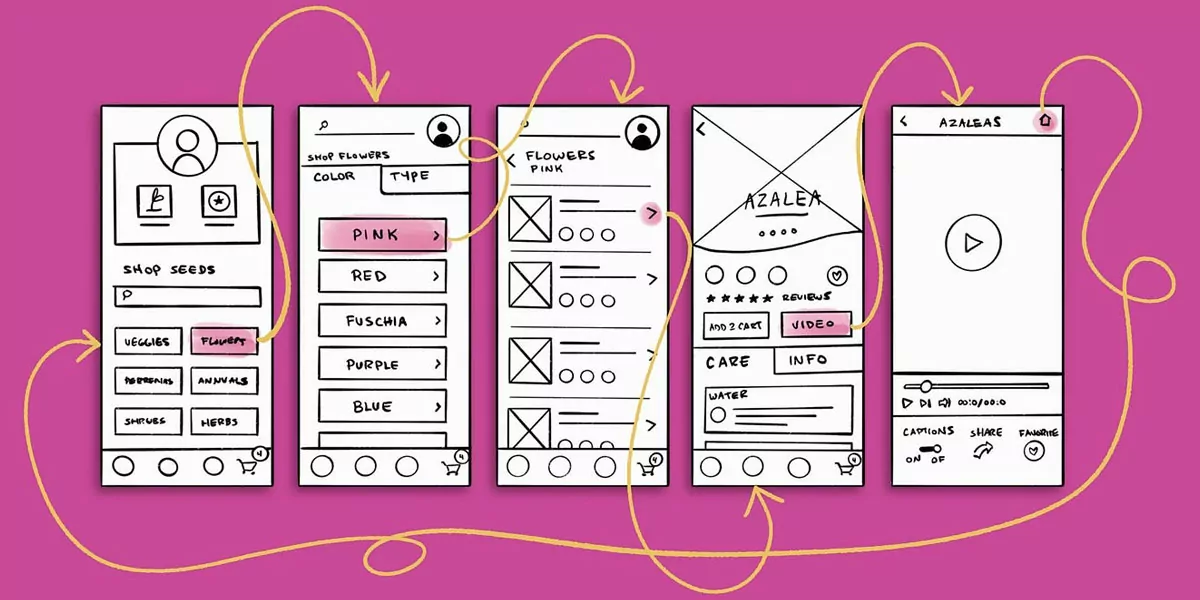
Low-fidelity wireframes serve as a starting point for the design process, providing a visual framework for the content and functionality of a digital product. They help designers explore different layout options and ensure that the user experience is prioritized before investing time and resources into high-fidelity mockups.
By working on low-fidelity wireframes early on, designers can identify and address any potential design issues or usability concerns in the initial stages. This saves time, effort, and resources by avoiding major design revisions later in the process. Low-fidelity wireframes act as a communication tool, allowing designers to share their vision with stakeholders and gather valuable feedback before diving into the detailed design phase.
The Importance of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Benefits of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Time and Cost Savings
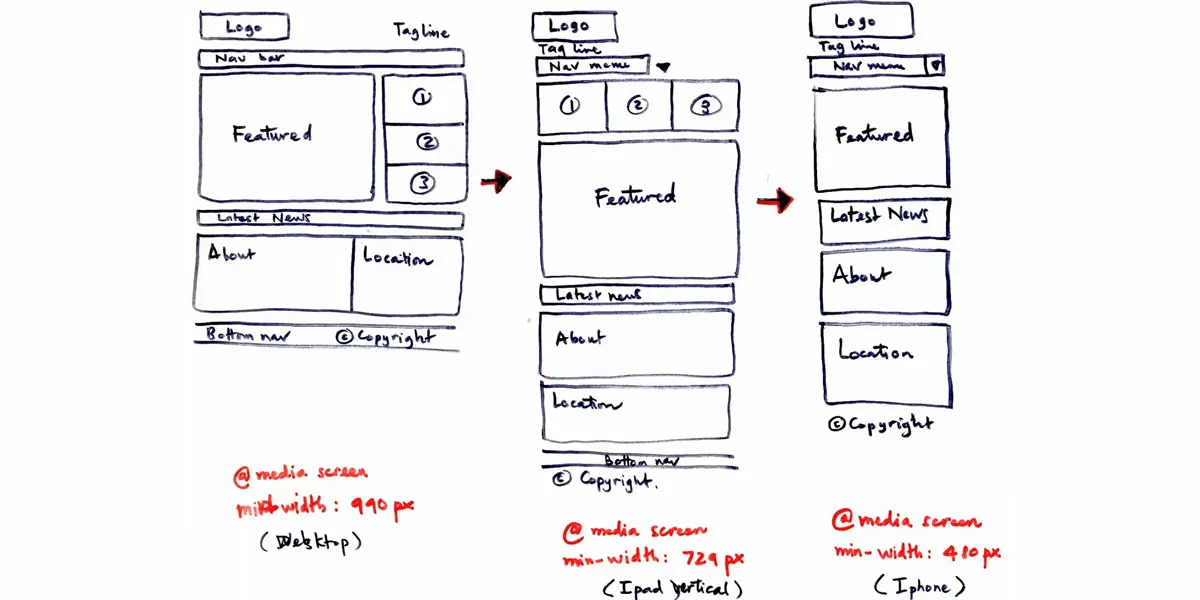
One of the significant benefits of using low-fidelity wireframes is the time and cost savings they offer. These wireframes enable designers to quickly iterate and experiment with different ideas without getting caught up in the details. By focusing on the overall structure and functionality, designers can avoid wasting time on intricate design elements that might change or be discarded later in the process. This rapid ideation process helps in streamlining the design workflow, ultimately reducing costs and accelerating project timelines.
Early Concept Validation
Low-fidelity wireframes act as a valuable tool for early concept validation. By creating these wireframes, designers can gather feedback from stakeholders and users at an early stage. These wireframes serve as a conversation starter, enabling discussions about the overall structure, content prioritization, and user flows. By involving stakeholders and users in the process, designers can ensure that the final design meets their expectations and addresses their needs effectively.
Unpredictability Mitigation
Designing a digital product involves numerous creative decisions, and sometimes ideas can be unpredictable. Low-fidelity wireframes help identify potential usability issues and uncover design flaws early on. By focusing on the core layout and functionality, designers can eliminate unpredictable ideas and ensure a smoother transition to the next design phases. This iterative approach saves time, effort, and resources by addressing design issues before investing heavily in high-fidelity visuals.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Low-fidelity wireframes provide designers with the freedom to experiment and iterate quickly. They can easily make changes, rearrange elements, and explore different design variations without being tied down by complex visuals or specific details. This flexibility allows designers to explore multiple design options, gather feedback, and refine their ideas without significant constraints. Low-fidelity wireframes serve as a dynamic tool that adapts to the evolving needs and preferences of the design process.
Benefits of Low-Fidelity Wireframes
How to Create Low-Fidelity Wireframes
To create effective low-fidelity wireframes, follow these step-by-step instructions:
1. Define the Scope
Before starting the wireframing process, clearly define the objectives and scope of your project. Understand the target audience, user goals, and project requirements. This will ensure that your wireframes focus on the essential elements and functionality.
2. Start with Sketching
Begin by sketching the wireframe using pen and paper or a digital sketching tool. Start with a rough outline, capturing the main sections, content blocks, and key interactions. This initial sketching phase allows you to quickly explore different layout possibilities.
3. Use Basic Shapes and Symbols
Represent different elements using simple shapes and symbols. For example, use rectangles for images, circles for buttons, and lines for text blocks. Focus on capturing the overall structure and layout rather than specific design details.
4. Focus on Hierarchy and Flow
Establish a clear hierarchy and flow of information within your wireframe. Use size and positioning to indicate the importance and order in which users will interact with different elements. Emphasize the key elements and prioritize content based on user needs.
5. Add Annotations
Include explanatory notes and annotations to clarify any interactions, functionalities, or specific design considerations. Annotations help stakeholders and developers understand the intended functionality and provide additional context to your wireframes.
6. Leverage Digital Tools
If you prefer digital wireframing tools, there are numerous options available such as Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, and Balsamiq. These tools provide pre-built UI elements and templates for faster wireframe creation. They also offer features like interactive prototyping, collaboration, and easy sharing of wireframes with stakeholders.
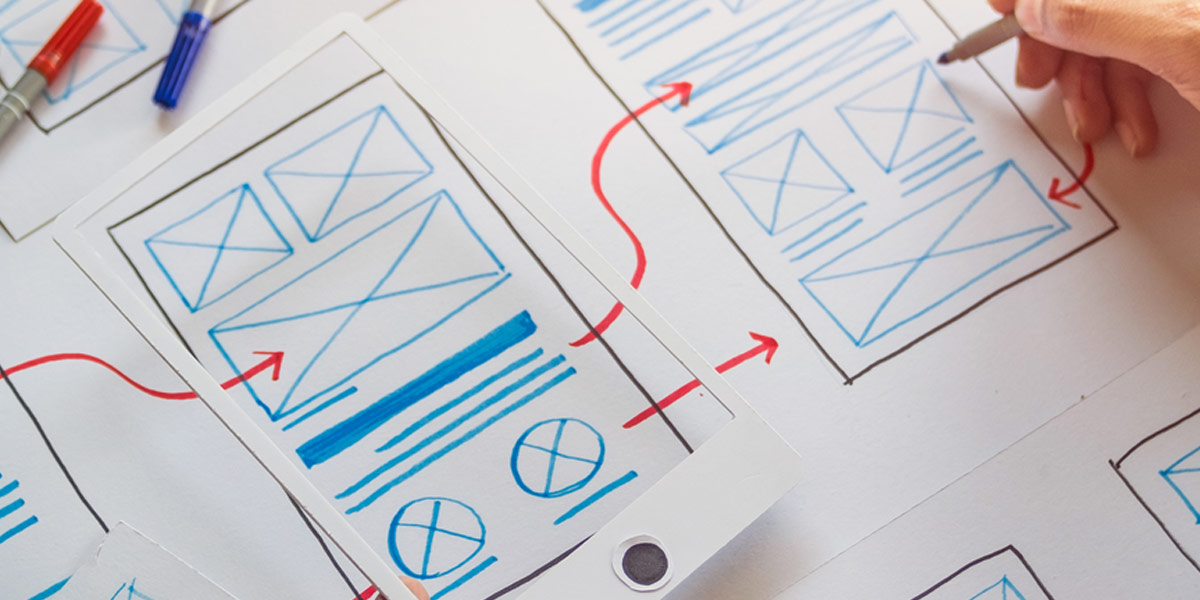

How to Create Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Best Practices for Using Low-Fidelity Wireframes
To make the most out of low-fidelity wireframes, consider the following best practices:
Iterate and Refine
Treat low-fidelity wireframes as a work in progress. Continuously gather feedback, iterate on your designs, and refine them based on user and stakeholder input. Use wireframes as a starting point and keep refining them as you progress through the design process.
Communicate Intent
When presenting your wireframes, clearly communicate that they are low fidelity and focus on structure rather than aesthetics. This will prevent unnecessary distractions and ensure that the feedback you receive is relevant to the wireframe stage.
Collaborate with Stakeholders
Involve stakeholders early in the process to align expectations and gain valuable insights. Collaboration fosters a shared understanding and increases the chances of delivering a successful final design. Seek input from stakeholders, including developers, project managers, and marketing teams, to incorporate their perspectives into the wireframing process.
Consider User Needs
Always keep the end user in mind. Ensure that your wireframes address their needs, goals, and pain points. Incorporate user-centred design principles and usability considerations to create wireframes that prioritize a positive user experience.

Best Practices for Using Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Conclusion
In conclusion, low-fidelity wireframes are essential tools in the design process, allowing designers to quickly visualize and iterate on the layout and structure of websites and applications. By embracing the simplicity of low-fidelity wireframes, designers can save time, reduce costs, validate concepts, and mitigate unpredictability. Remember to leverage these wireframes as a starting point for discussions, gather feedback, and refine them before moving on to high-fidelity mockups. Incorporating low-fidelity wireframes into your design workflow can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your design process.
FAQs
What are low-fidelity wireframes?
Low-fidelity wireframes are simple and rough sketches that outline the basic elements and structure of a webpage or application. They serve as a visual representation of the layout and functionality before moving into the detailed design phase.
How are low-fidelity wireframes different from high-fidelity wireframes?
Low-fidelity wireframes focus on the overall structure and functionality of a design, while high-fidelity wireframes are more detailed and refined, incorporating visual aesthetics, colours, and specific design elements. Low-fidelity wireframes are quick and minimalistic, whereas high-fidelity wireframes are more polished and resemble the final product closely.
What are the benefits of using low-fidelity wireframes?
Using low-fidelity wireframes offers several benefits. They help save time and cost by allowing designers to iterate and experiment quickly without getting caught up in intricate details. Low-fidelity wireframes also facilitate early concept validation, as they serve as conversation starters for discussions with stakeholders and users. They help mitigate unpredictability in design ideas and offer flexibility and adaptability throughout the design process.
How do you create low-fidelity wireframes?
To create low-fidelity wireframes, you can start by defining the scope and objectives of your project. Then, sketch the wireframe using pen and paper or a digital sketching tool, focusing on the overall structure and layout. Use basic shapes and symbols to represent different elements and prioritize hierarchy and flow. Don’t forget to add annotations to provide clarity, and leverage digital tools if preferred.
What are the best low-fidelity wireframe tools available in the market?
There are several excellent low-fidelity wireframe tools available in the market. Some popular options include Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, and Balsamiq. These tools provide pre-built UI elements, templates, and interactive prototyping features that streamline the wireframing process and enhance collaboration among design teams.

With over two decades of web design and development expertise, I craft bespoke WordPress solutions at FallingBrick, delivering visually striking, high-performing websites optimised for user experience and SEO.




