User experience (UX) design plays a crucial role in creating intuitive and user-friendly digital products. In today’s competitive landscape, businesses recognize the importance of providing exceptional user experiences to attract and retain customers. In this article, we will explore the key principles and best practices of UX design that can help you create engaging and effective digital experiences for your users.

UX Design Principles and Best Practices
UX Principles to Boost Your Design Practice Introduction
User experience design focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and enjoyment of a product or service. It involves understanding users’ needs, goals, and behaviours to create meaningful and valuable interactions. UX design encompasses various disciplines such as interaction design, information architecture, visual design, and usability testing.
Understanding User Experience
Defining User Experience
User experience refers to the overall perception and feelings a person has when interacting with a product or system. It encompasses the user’s emotions, attitudes, and behaviours before, during, and after using a product. A positive user experience leads to higher user satisfaction, increased engagement, and improved brand loyalty.
Importance of User Experience
Investing in user experience design is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps businesses differentiate themselves from competitors by offering superior experiences. Secondly, a positive user experience leads to higher conversion rates and customer retention. Lastly, a well-designed user experience reduces support costs by minimizing user errors and confusion.
UX Design Principles
To create exceptional user experiences, designers adhere to certain principles. These principles guide the decision-making process and ensure that the design is user-centred and effective. Let’s explore some of the key principles of UX design:
Simplicity and Clarity
Simplicity is a fundamental principle of UX design. Keeping interfaces clean, uncluttered, and intuitive helps users accomplish their tasks efficiently. By reducing complexity and unnecessary elements, designers can create a seamless and enjoyable experience for users.
Consistency
Consistency in design ensures that users can easily understand and predict how different elements will behave. It involves using consistent visual and interaction patterns throughout the product, such as using the same colours, typography, and icons. Consistency fosters familiarity, reduces cognitive load, and improves usability.
User-Centred Design
The user-centred design focuses on understanding users’ goals, needs, and behaviours to create products that meet their expectations. It involves conducting user research, creating user personas, and involving users throughout the design process. By placing the user at the centre of the design, designers can create experiences that resonate with their target audience.
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy refers to the arrangement of elements in a design to convey their importance and guide users’ attention. By utilizing visual cues such as size, colour, and contrast, designers can create a clear hierarchy that directs users’ focus and helps them navigate the interface effectively.
Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that digital products are usable by individuals with disabilities. Designers should consider factors such as colour contrast, alternative text for images, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility. By designing for accessibility, designers can make their products inclusive and reach a wider audience.
UX Design Principles
Best Practices for UX Design
While UX design principles provide a solid foundation, implementing best practices is crucial for creating exceptional user experiences. Let’s explore some of the best practices for UX design:
Conducting User Research
User research involves gathering insights about users’ behaviours, needs, and preferences. Through methods such as surveys, interviews, and observations, designers can gain valuable information to inform their design decisions. User research helps identify pain points, uncover user motivations, and validate design concepts.
Creating User Personas
User personas are fictional representations of target users that help designers understand their goals, preferences, and behaviours. By creating detailed personas, designers can design with specific user needs in mind and create experiences that resonate with their target audience.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping allow designers to create low-fidelity representations of the final product. These visual representations help visualize the structure, layout, and flow of the interface. Iteratively testing and refining wireframes and prototypes allow designers to gather feedback early in the design process and make informed design decisions.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product to identify usability issues. By testing prototypes or existing products with real users, designers can uncover pain points, understand user behaviour, and validate design choices. Usability testing helps improve the overall user experience and ensures that the design meets user expectations.
Iterative Design Process
The iterative design process involves continuously refining and improving a design based on user feedback and testing results. By adopting an iterative approach, designers can address issues and make incremental improvements over time. This process allows for continuous learning and optimization of the user experience.
Responsive Design
With the increasing use of mobile devices, designing for responsive experiences is crucial. Responsive design ensures digital products adapt and display appropriately across different screen sizes and devices. By considering the limitations and capabilities of various devices, designers can create consistent experiences that cater to a wide range of users.
Microinteractions
Microinteractions are subtle, single-purpose interactions that provide feedback and enhance the overall user experience. Examples include button animations, loading spinners, or progress indicators. Well-designed micro-interactions add delight, engage users, and make the interaction feel more human and responsive.
Error Handling
Error handling is a critical aspect of UX design. Designers should anticipate and handle errors gracefully by providing clear error messages, suggestions for resolution, and assistance in recovering from errors. Effective error handling reduces user frustration and helps maintain a positive user experience.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing performance is essential for delivering a smooth and fast user experience. Designers should prioritize optimizing page load times, minimizing the use of unnecessary animations or effects, and ensuring the product functions well on various devices and network conditions. Performance optimization contributes to user satisfaction and encourages user engagement.
Feedback and Notifications
Providing timely feedback and notifications helps users stay informed and engaged with the product. Designers should incorporate clear and contextual feedback messages to confirm user actions, inform about system status, and guide users through processes. Well-designed feedback and notifications enhance the user experience and reduce user uncertainty.
Content Strategy
Content plays a crucial role in user experience. Designers should collaborate with content strategists to ensure that the content is concise, relevant, and well-structured. Using appropriate typography, formatting, and hierarchy helps users scan and digest information easily. A well-executed content strategy enhances the overall user experience.
Navigation Design
Navigation design focuses on creating intuitive and easy-to-use navigation systems that help users navigate the product seamlessly. Designers should consider user mental models, incorporate clear labels, and provide hierarchical structures to enable efficient exploration and discoverability. Effective navigation design simplifies user journeys and enhances the overall user experience.

Best Practices for UX Design
Designing for Mobile UX
With the widespread use of mobile devices, designing for mobile user experiences is vital. Let’s explore some best practices for designing mobile experiences:
Mobile-First Approach
A mobile-first approach involves designing for mobile devices first and then adapting the design for larger screens. This approach ensures that the essential content and functionalities are prioritized for smaller screens, providing a better user experience on mobile devices.
Responsive Layouts
Using responsive layouts enables designs to adapt to different screen sizes and orientations. Designers should consider fluid grids, flexible images, and breakpoints to ensure that the design remains usable and visually appealing across various devices.
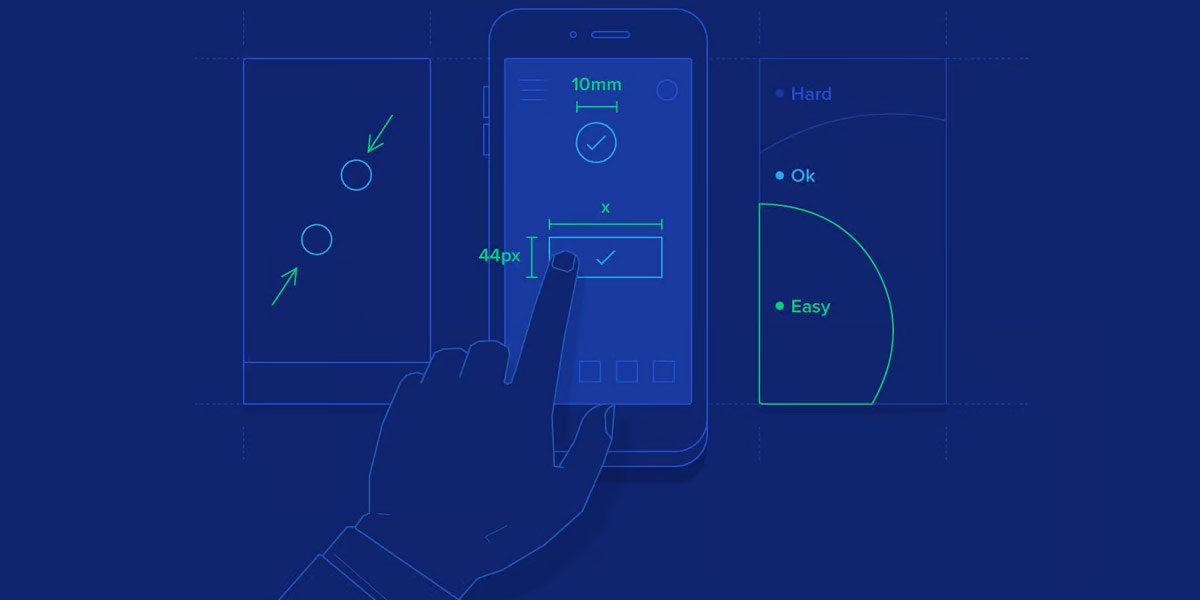
Gestures and Touch Targets
Designing with gestures and touch targets in mind enhances mobile usability. Designers should consider the size of touch targets, provide visual affordances for interactive elements, and utilize gestures that are intuitive and widely understood by users.
Mobile Navigation Patterns
Navigation patterns for mobile devices should prioritize simplicity and ease of use. Designers can use patterns such as bottom navigation bars, hamburger menus, or swipe gestures to provide intuitive and accessible navigation experiences.
Designing for Mobile UX
Enhancing UX with Visual Design
Visual design plays a significant role in shaping the user experience. Let’s explore some ways to enhance UX through visual design:
Typography
Choosing appropriate typography helps create a visually appealing and readable interface. Designers should consider factors such as font size, typeface, line spacing, and hierarchy to ensure that the text is legible and complements the overall design.
Colour Theory
Colour influences user emotions, perceptions, and interactions. Designers should use colours strategically to create visual interest, convey meaning, and establish a consistent visual identity. Understanding colour theory helps designers create harmonious and accessible colour palettes.
Imagery and Icons
Images and icons add visual interest and aid in conveying information. Designers should use high-quality and relevant images that support the content and align with the brand identity. Icons should be simple, recognizable, and consistent with established conventions to ensure ease of understanding.
Visual Consistency
Maintaining visual consistency throughout the product helps establish a cohesive and professional user experience. Designers should follow established design patterns, use consistent styles, and ensure that visual elements align with the overall brand guidelines.
Incorporating UX in E-commerce
Creating a seamless user experience is vital in e-commerce to drive conversions and customer satisfaction. Let’s explore how to incorporate UX design in e-commerce:
Product Discovery and Search
Designing intuitive product discovery features, such as advanced search filters, sorting options, and personalized recommendations, helps users find products quickly. Clear product descriptions, high-quality images, and user reviews also contribute to a positive shopping experience.
Seamless Checkout Process
Streamlining the checkout process reduces cart abandonment and improves conversion rates. Designers should minimize the number of steps, provide progress indicators, offer guest checkout options, and simplify form fields to create a frictionless checkout experience.
Persuasive Design Techniques
Persuasive design techniques, such as scarcity, social proof, and persuasive copywriting, can influence user behaviour and drive conversions. Designers should carefully incorporate these techniques to create a sense of trust, urgency, and value for users.
UX Design for Web Applications
Web applications often have complex functionalities and require thoughtful UX design. Let’s explore some best practices for designing web application experiences:
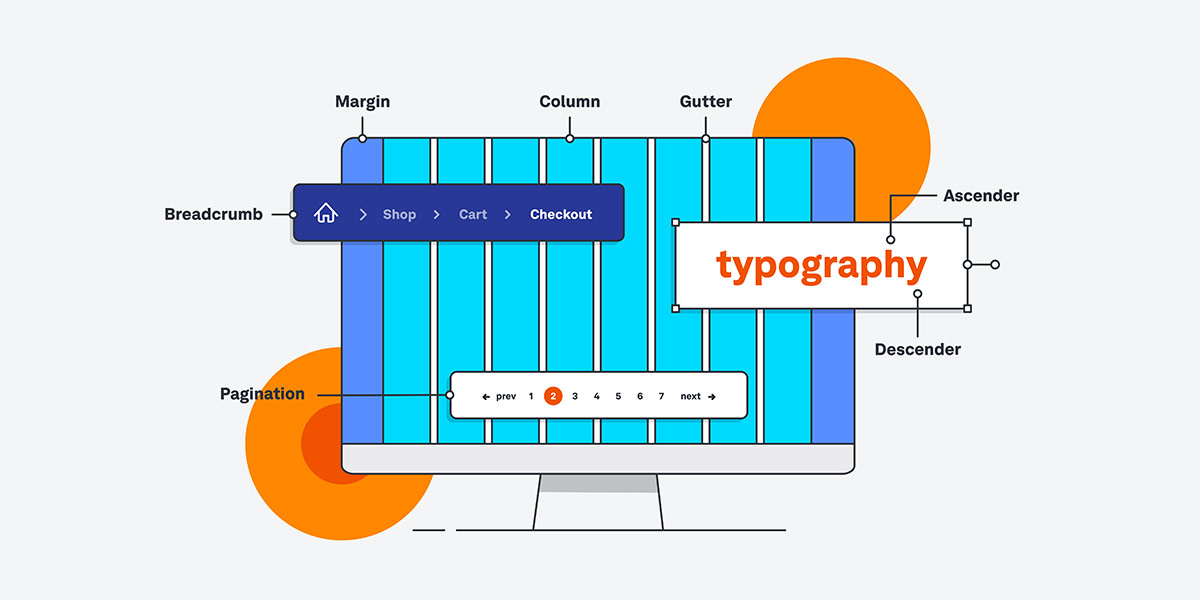
Information Architecture
Creating a well-structured information architecture helps users navigate complex web applications effectively. Designers should organize content hierarchically, provide clear labelling, and implement intuitive navigation systems to improve the discoverability of features and functionalities.
Form Design and Validation
Designing user-friendly forms ensures that users can input information accurately and efficiently. Designers should use appropriate form field types, provide helpful error messages, and offer real-time validation to guide users through the form completion process.
Onboarding and User Engagement
Onboarding experiences introduce users to the key features and benefits of a web application. Designers should design intuitive onboarding flows that guide users through the initial setup and provide contextually relevant information. Additionally, incorporating gamification or interactive elements can enhance user engagement.
Dashboard and Data Visualization
Designing effective dashboards and data visualization components helps users make sense of complex data and monitor key metrics. Designers should prioritize relevant information, use visual cues to highlight trends or anomalies and provide customization options to tailor the experience to individual users’ needs.
UX Design for Web Applications
Measuring UX Success
Measuring the success of UX design is crucial to identify areas for improvement and ensuring that design decisions align with user expectations. Let’s explore some methods for measuring UX success:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Defining and tracking key performance indicators helps evaluate the impact of UX design on business goals. Metrics such as conversion rates, time on task, user engagement, and user satisfaction provide insights into the effectiveness of the user experience.
User Satisfaction Surveys
Conducting user satisfaction surveys allows designers to gather direct feedback from users. Surveys can measure user satisfaction, identify pain points, and uncover areas for improvement. Using validated survey scales and open-ended questions provides valuable insights into user perceptions and preferences.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Conversion rate optimization focuses on improving the rate at which users complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. By conducting A/B testing, analyzing user behaviour, and making iterative improvements, designers can optimize the user experience and increase conversions.
A/B Testing
A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a design to determine which performs better in terms of user engagement or conversion rates. By testing variations of design elements, layouts, or copy, designers can make data-driven decisions and continuously refine the user experience.
The Future of UX Design
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the future of UX design holds exciting possibilities. Here are some key trends and advancements that are shaping the future of UX design:
Voice User Interfaces (VUI)
Voice user interfaces are becoming increasingly prevalent with the rise of virtual assistants and smart speakers. Designers will need to explore new ways of creating conversational and intuitive experiences that leverage natural language processing and voice recognition technologies.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are transforming the way users interact with digital content. UX designers will be able to create immersive and interactive experiences that blend the virtual and physical worlds, opening up new possibilities in fields such as gaming, education, and e-commerce.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of connected devices in our daily lives presents unique challenges and opportunities for UX design. Designers will need to create seamless and intuitive experiences that span across multiple devices and touchpoints, ensuring that users can easily interact with and control their interconnected devices.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML technologies are revolutionizing UX design by enabling personalized and predictive experiences. Designers can leverage AI algorithms to analyze user data, make intelligent recommendations, and automate certain tasks, ultimately delivering tailored experiences that anticipate user needs.
Ethical and Inclusive Design
As technology becomes more deeply integrated into our lives, ethical and inclusive design principles will become increasingly important. Designers will need to prioritize privacy, data security, and accessibility, ensuring that their designs consider diverse user perspectives and empower all individuals to access and use digital products and services.
Emotional Design
The emotional design focuses on creating experiences that evoke positive emotions and establishes a connection with users on a deeper level. Designers will explore techniques to evoke emotions through visual aesthetics, micro-interactions, storytelling, and personalized experiences, aiming to create memorable and engaging interactions.
Designing for Multimodal Interfaces
With the convergence of various interface modalities such as touch, voice, gesture, and eye-tracking, designers will need to consider how users interact with multiple modalities simultaneously. Designing for multimodal interfaces will require a holistic approach that ensures seamless transitions and coherent interactions across different modes.
Data-Driven Design Decisions
Data-driven design decisions will continue to gain importance in the future of UX design. Designers will rely on user analytics, user testing, and other quantitative and qualitative data sources to inform their design choices and validate the effectiveness of their designs, ensuring continuous improvement and optimization.
UX Design Principles and Best Practices: The Future of UX Design
Conclusion
In conclusion, UX design principles and best practices are essential for creating exceptional user experiences. Designers can create intuitive and engaging interfaces by incorporating principles like simplicity, consistency, user-centred design, and visual hierarchy. Best practices such as user research, wireframing, prototyping, usability testing, and an iterative design process help refine the user experience and ensure it aligns with user expectations. Whether designing for mobile experiences, e-commerce, web applications, or incorporating persuasive design techniques, considering the unique requirements of each context contributes to successful UX design. By measuring UX success through KPIs, user satisfaction surveys, and conversion rate optimization, designers can continuously improve the user experience and drive business outcomes.
FAQs
Why is UX design important?
UX design is important because it focuses on creating products that meet users’ needs and expectations. A well-designed user experience improves user satisfaction, drives engagement, and contributes to the success of digital products or services.
How can I improve the usability of my website?
To improve website usability, consider conducting user research, simplifying navigation, optimizing page load times, providing clear content and call-to-action, and testing the website with real users to identify and address usability issues.
What role does visual design play in UX?
Visual design plays a crucial role in UX by shaping the overall look and feel of a product or interface. It includes elements such as typography, colour, imagery, and layout, which contribute to the aesthetic appeal and usability of the design.
How can I optimize the mobile user experience?
To optimize the mobile user experience, adopt a mobile-first approach, use responsive layouts, design intuitive touch targets and gestures, prioritize performance optimization, and ensure seamless navigation and content visibility on smaller screens.
How do I measure the success of my UX design?
Measuring the success of UX design involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting user satisfaction surveys, performing conversion rate optimization (CRO), and utilizing A/B testing to make data-driven decisions and improvements based on user feedback.

With over two decades of web design and development expertise, I craft bespoke WordPress solutions at FallingBrick, delivering visually striking, high-performing websites optimised for user experience and SEO.




